ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Extreme Gradient Boosting Driven Intelligent System for Tomato Leaf Disease Identification
1
Department of Computing and Information Technology, The University of the West Indies, St Augustine, 330912, St Augustine, Trinidad and Tobago
2
Department of Life Sciences, The University of the West Indies, St Augustine, 330912, St Augustine, Trinidad and Tobago
These authors had equal contribution to this work
A - Research concept and design; B - Collection and/or assembly of data; C - Data analysis and interpretation; D - Writing the article; E - Critical revision of the article; F - Final approval of article
Submission date: 2025-05-23
Acceptance date: 2025-09-10
Online publication date: 2025-11-05
Corresponding author
VIJAYANANDH RAJAMANICKAM
Department of Computing and Information Technology, The University of the West Indies, St Augustine, 330912, St Augustine, Trinidad and Tobago
Department of Computing and Information Technology, The University of the West Indies, St Augustine, 330912, St Augustine, Trinidad and Tobago
HIGHLIGHTS
- Focus on major regional diseases prevalent in the Caribbean
- Applied advanced image preprocessing to improve image quality
- Extracted comprehensive features including color histograms, LBP and GLCM
- Trained 11,979 images from PlantVillage dataset and achieved an accuracy of 97.20%
- Effective and accurate disease identification achieved with XGBoost
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
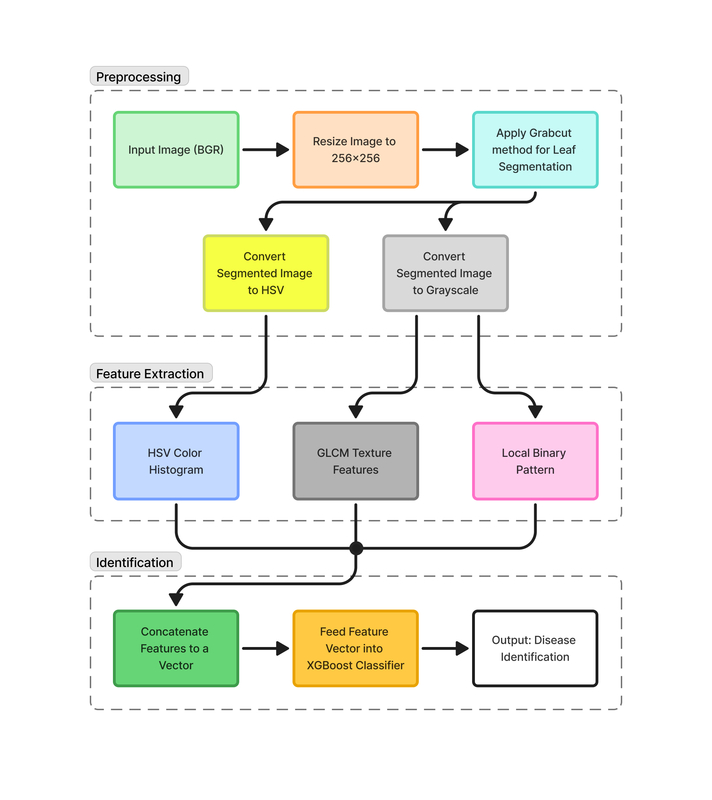
Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) is an important vegetable crop, which is susceptible to multiple diseases that can impact yield and produce quality. The current research aims to classify major tomato diseases in the Caribbean region through an intelligent system developed. The system is based on six key diseases including bacterial spot, early blight, late blight, septoria leaf spot, yellow leaf curl virus, and mosaic virus. To improve the identification accuracy, all images were first resized and then segmented using the GrabCut method to isolate the leaf regions. The segmented images were subsequently converted to HSV color space and grayscale before feature extraction was performed. A total of 96 features were extracted, including color histograms, Local Binary Pattern (LBP), and Gray-Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM). The Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) algorithm was employed for disease identification. This study uses a dataset of 11,979 images from the PlantVillage collection, including both healthy and diseased samples, and the developed model achieved a disease identification accuracy of 97.20% while remaining computationally efficient.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have declared that no conflict of interests exist.
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.