REVIEW
Constitutive and induced plant defense mechanisms against pathogens: A review
1
Department for plant physiology, Faculty of Agriculture and Food Sciences, Zmaja od Bosne 8, 71 000, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina
A - Research concept and design; B - Collection and/or assembly of data; C - Data analysis and interpretation; D - Writing the article; E - Critical revision of the article; F - Final approval of article
Submission date: 2025-06-27
Acceptance date: 2025-10-27
Online publication date: 2025-11-04
Corresponding author
Senad Murtić
Department for plant physiology, Faculty of Agriculture and Food Sciences, Zmaja od Bosne 8, 71 000, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Department for plant physiology, Faculty of Agriculture and Food Sciences, Zmaja od Bosne 8, 71 000, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina
HIGHLIGHTS
- • Pattern recognition receptors are responsible for sensing the presence of pathogens
- • Constitutive defenses include barriers that exist before pathogen attack
- • The induced defense responses in plants are activated upon pathogen recognition
- • Phytoalexins are biosynthesized by plants in response to pathogen attack
- • Pathogenesis-related proteins are able to prevent the spread of the pathogen
KEYWORDS
Biotic stressEffector-triggered immunity (ETI)Host-pathogen interactionPAMP-triggered immunity (PTI)Pathogenesis-related proteins
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
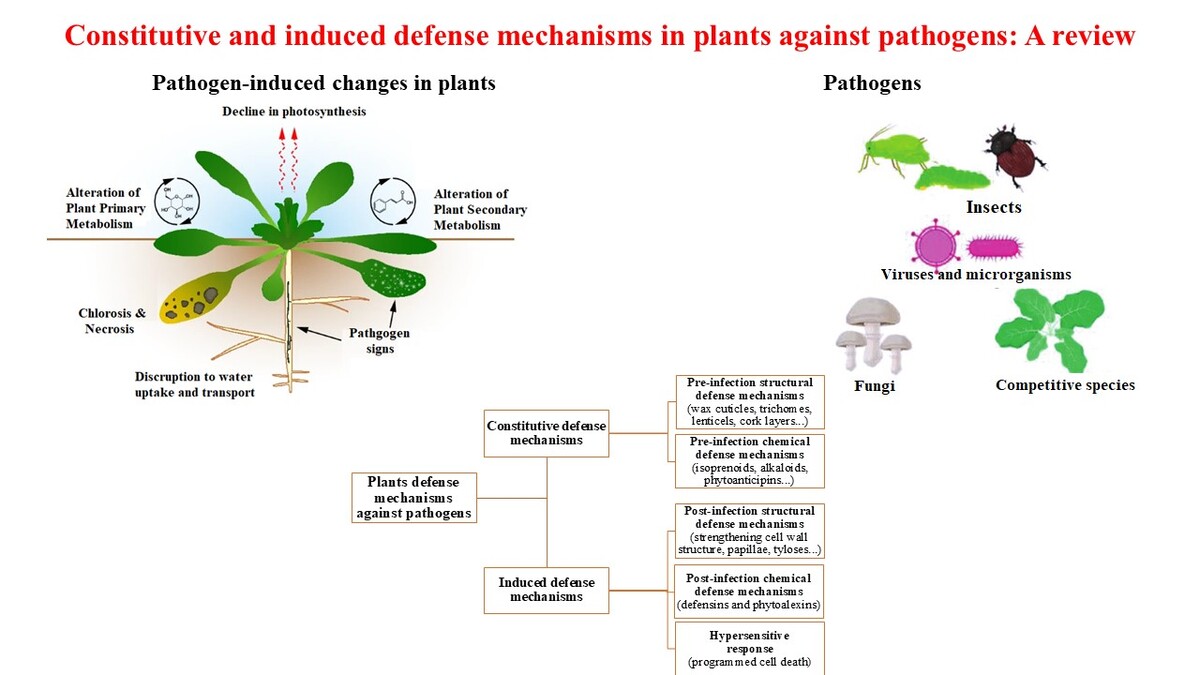
Plants are frequently exposed to diverse pathogens such as bacteria, fungi, viruses, and nematodes. Understanding the mechanisms by which plants recognize pathogen attacks and mount defensive responses is crucial for enhancing plant resistance. This review summarizes current knowledge on the effects of pathogen infection on plant growth and development, as well as the mechanisms that plants use to minimize their adverse effects. Additionally, this review offers valuable insights into the mechanisms of host-pathogen interaction, which are key to developing effective disease control strategies. Plant defenses can be broadly categorized into constitutive and induced mechanisms. Constitutive defenses include pre-formed physical barriers like cuticles and cell walls, as well as chemical deterrents such as unfavorable pH and nutrient limitation. Induced defense mechanisms are activated in response to pathogen detection and involve processes such as cell wall fortification, rapid programmed cell death at the infection site, and the synthesis of pathogenesis-related proteins that degrade invading pathogens. Advances in understanding these defense mechanisms offer essential guidance for developing effective strategies to protect agricultural crops from pathogens.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have declared that no conflict of interests exist.
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.