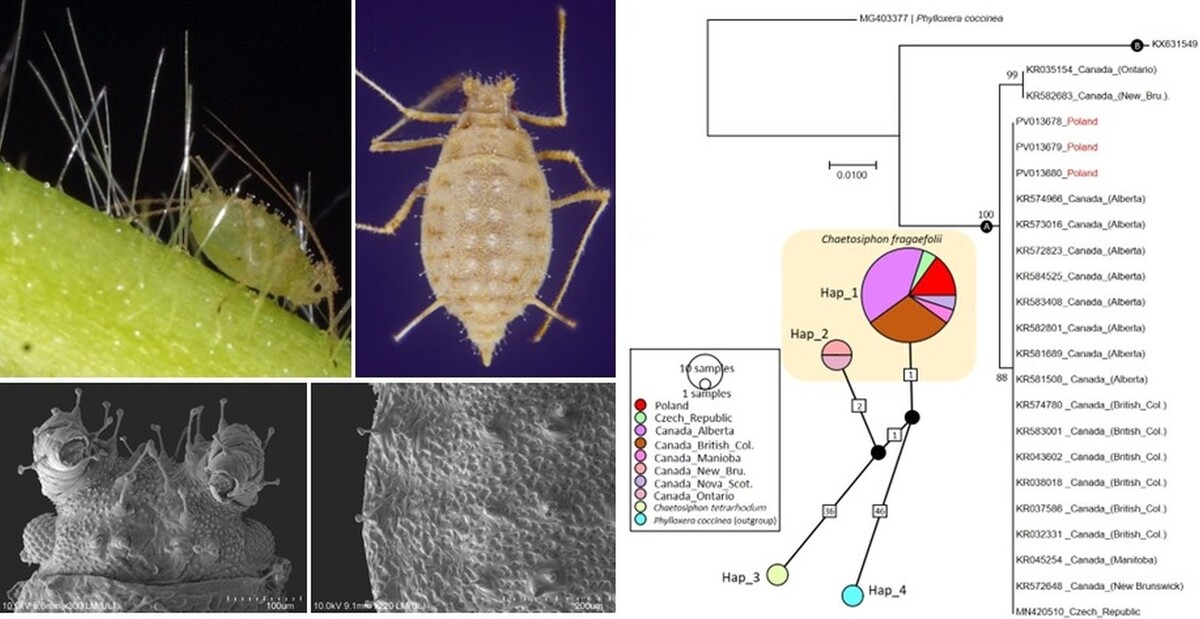
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Morphological and molecular insights into the invasive strawberry aphid Chaetosiphon fragaefolii –
a critical pest and virus vector new to Poland
1
Faculty of Natural Sciences, Institute of Biology, Biotechnology and Environmental Protection, University of Silesia in Katowice, Katowice, Poland
2
Insect Biosystematics Laboratory, Department of Agricultural Biotechnology, Research Institute of Agricultural and Life Sciences, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea (South)
A - Research concept and design; B - Collection and/or assembly of data; C - Data analysis and interpretation; D - Writing the article; E - Critical revision of the article; F - Final approval of article
Submission date: 2025-03-08
Acceptance date: 2025-05-20
Online publication date: 2025-11-25
Corresponding author
Mariusz Kanturski
Faculty of Natural Sciences, Institute of Biology, Biotechnology and Environmental Protection, University of Silesia in Katowice, Katowice, Poland
Faculty of Natural Sciences, Institute of Biology, Biotechnology and Environmental Protection, University of Silesia in Katowice, Katowice, Poland
Journal of Plant Protection Research 2025;65(4):548-560
HIGHLIGHTS
- First record of Chaetosiphon fragaefolii in Poland
- Characteristics to distinguish strawberry aphid from other species presented
- SEM analysis performed for the first time,
- Molecular haplotype analysis for the first time
- The invasion route shown for the first time
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
The present research reports the first record in Poland of the alien invasive and quarantine
species Chaetosiphon (Pentatrichopus) fragaefolii (Cockerell, 1901) – the strawberry aphid.
Native to North America, it is a critical pest and viral vector associated with strawberry
crops. This study provides valuable insights into the genetic and morphological characteristics
of the strawberry aphid. By integrating morphological and molecular analyses,
the taxonomic resolution has been improved and deepened the understanding of this economically
important species, particularly its genetic diversity, distribution, and potential
invasion routes. For the first time, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analyses were performed
to elucidate the general morphology, chaetotaxy, and sensilla of the antennae and
mouthparts of this species, providing a better understanding in the context of its natural
and chemical control.
RESPONSIBLE EDITOR
Beata Borowiak-Sobkowiak
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have declared that no conflict of interests exist.
REFERENCES (72)
1.
Alford D.V. 1976. Some observations on the effect of pests on strawberry yields. Annals of Applied Biology 84 (3): 440–444.
2.
Alford D.V. 2007. Pests of Fruit Crops: A Color Handbook. Boston-San Diego, Academic Press, 461 pp.
3.
Alford D.V. 2012. Pests of Ornamental Trees, Shrubs and Flowers: A Color Handbook. 2nd ed., Academic Press, UK.
4.
Balachowsky A. 1933. I. Sur la présence en France de Capitophorus fragaefolii Ckll., Aphide nouvellement introduit et nuisible au frasier. II. Sur l’existence de nouveaux foyers d’Aphis forbesi Weed. Revue de Pathologie Végétale et d’Entomologie gricole de France 20: 250–267.
5.
Barjadze S., Halbert S.E., Moore M.R., Kanturski M. 2022. Morphology, molecular phylogenetics, and DNA barcoding revealed new unusual species of the aphid genus Pleotrichophorus from the USA (Insecta, Hemiptera: Aphididae). Zootaxa 5183 (1): 390–422. DOI: https://doi.org/10.11646/zoota....
6.
Blackman R.L. 2010. Aphids – Aphidinae (Macrosiphini). Handbooks for Identifying of British Insects 2: 1–413.
7.
Blackman R.L., Eastop V.F. 2000. Aphids on the World’s Crops (2nd ed). Wiley, Chichester, 466 pp.
8.
Blackman R.L., Eastop V.F. 2006. Aphids on the World’s Herbaceous Plants and Shrubs. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, England, 1493 pp.
9.
Brault V., Uzest M., Monsion B., Jacquot E., Blanc S. 2010. Aphids as transport devices for plant viruses Les pucerons, un moyen de transport des virus de plante. Comptes Rendus Biologies 333: 524–538.
10.
Cédola C., Greco N. 2010. Presence of the aphid, Chaetosiphon fragaefolii, on strawberry in Argentina. Journal of Insect Science 10 (1): 109.
11.
Choi H., Shin S., Jung S., Clarke D.J., Lee S. 2018. Molecular phylogeny of Macrosiphini (Hemiptera: Aphididae): An evolutionary hypothesis for the Pterocomma-group habitat adaptation. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 121: 12–22.
12.
Clement M., Posada D., Crandall K.A. 2000. TCS: a computer program to estimate gene genealogies. Molecular Ecology 9 (10): 1657–1660.
13.
Cockerell T.D.A. 1901. A new plant-louse injuring strawberry plants in Arizona. The Canadian Entomologist 33 (4): 101.
14.
Coeur d’acier A., Pérez Hidalgo N., Petrović-Obradović O. 2010. Aphids (Hemiptera, Aphididae). Chapter 9.2. p. 435–474. In: “Alien terrestrial arthropods of Europe” (A. Roques et al., eds.). BioRisk 4 (1): 435–474.
15.
Eastop V.F. 1983. The biology of the principle virus vectors. p. 115–132. In: “Plant Virus Epidemiology: the Spread and Control. of Insect-Borne Viruses” (R.T. Plumb, J.M. Thresh, eds). Oxford, Blackwell Scientific Publications.
17.
Foottit R.G., Maw H.E.L., von Dohlen C.D., Hebert P.D.N. 2008. Species identification of aphids (Insecta: Hemiptera: Aphididae) through DNA barcodes. Molecular Ecology Resources 8 (6): 1189–1201. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755....
18.
Fránová J., Přibylová J., Koloniuk I. 2019. Molecular and biological characterization of a new strawberry cytorhabdovirus. Viruses 11 (11): 982.
19.
Gwiazdowski R.A., Foottit R.G., Maw H.E.L., Hebert P.D.N. 2015. The Hemiptera (Insecta) of Canada: Constructing a Reference Library of DNA Barcodes. PLoS ONE 10 (4): e0125635. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journa....
20.
Guerrieri E., Digilio M.C. 2008. Aphid-plant interactions: a review. Journal of Plant Interactions 3 (4): 223–232. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/174291....
21.
Hebert P.D.N., Ratnasingham S., Zakharov E.V., Telfer A.C., Levesque-Beaudin V., Milton M.A., Pedersen S., Jannetta P., deWaard J.R. 2016. Counting animal species with DNA barcodes: Canadian insects. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B 371: 20150333. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2....
22.
Heie O.E. 1994. The Aphidoidea of Fennoscandia and Denmark V. Aphidinae. Part 2 of Macrosiphini. Fauna Entomologica Scandinavica 28: 1–242.
23.
Holman J. 2009. Host Plant Catalog of Aphids, Palaearctic Region. Springer Science + Business Media BV, 1216 pp.
24.
Hottes F.C., Frison T.H. 1931. The plant lice, or Aphidae, of Illinois. INHS Bulletin 19: 123–447.
26.
Hurley B.P., Garnas J., Wingfield M.J., Branco M., Richardson D.M. 2016. Slippers, B. Increasing numbers and intercontinental spread of invasive insects on eucalypts. Biological Invasions 18: 921–933.
27.
Ilharco F.A. 1973. Catalogue of the aphids of continental Portugal. In: Catalogo dos afídeos de Portugal continental. Oeiras, Mozambique: Estacao Agronomica Nacional, 134 pp.
28.
Ilharco F.A. 1984. The aphid fauna of Madeira: zoogeographical notes (Insecta, Homoptera, Aphidoidea). (Afidofauna madeirense: comentários zoogeográficos (Insecta, Homoptera, Aphidoidea).) Boletim da Sociedade Portuguesa de Entomologia. 14 (44): 149–157.
29.
Jensen A.S., Barjadze S., Kanturski M. 2020. A review of the aphid genus Macrosiphoniella del Guercio, 1911 (Hemiptera: Aphididae) in the USA with description of a new species. The European Zoological Journal 87: 412–443. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/247502....
30.
Kaszyca N., Mruk K., Kuna E., Taszakowski A., Depa Ł., Wojciechowski W. 2018. New data on the occurrence of aphids (Hemiptera: Aphidomorpha) in the Eastern Beskidy Mountains. Acta Entomologica Silesiana 26:1–8 (in Polish).
31.
Kanturski M., Mruk K., Morawski M., Wojciechowski W., Depa Ł. 2017. Nearctaphis bakeri (Cowen, 1895) and Illinoia liriodendri (Monell, 1879) – two aphid species (Hemiptera: Aphididae) of alien origin new to the Polish fauna. Annals of the Upper. Silesian Museum 26: 1–6.
32.
Kanturski M., Barjadze S. 2018. Hitherto unknown and poorly known morphs of Macrosiphoniella davazhamci and M. nikolajevi (Hemiptera: Aphididae) – aphid species new to Iran. Zootaxa 4524 (5): 536–552. DOI: https://doi.org/10.11646/zoota....
33.
Kanturski M., Stekolshchikov A.V. 2018. Rhinariaphis – A remarkable new aphid genus from Afghanistan (Hemiptera: Aphididae: Aphidinae). Zoologischer Anzeiger 277: 75–84. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcz.....
34.
Kanturski M., Lee Y., Depa Ł. 2018a. New records of an alien aphid species Tinocallis (Sappocallis) takachihoensis (Hemiptera, Aphididae, Calaphidinae) from countries in Central and Northern Europe. ZooKeys 730: 1–16. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3897/zookey....
35.
Kanturski M., Barjadze S., Jensen A.S., Wieczorek K. 2018b. A comparative morphological revision of the aphid genus Myzaphis van der Goot, 1913 (Insecta: Hemiptera: Aphididae) revealed a new genus and three new species. PLoS ONE 13 (3): e0193775.
36.
Kanturski M., Świątek P., Trela J., Borowiak-Sobkowiak B., Wieczorek K. 2020. Micromorphology of the model species pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum (Hemiptera, Aphididae) with special emphasis on the sensilla structure. The European Zoological Journal 87: 336–356. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/247502....
37.
Kanturski M., Barjadze S., Glumac A., Kaszyca-Taszakowska N. 2025. Stridulating species of Aphids of the genus Uroleucon (Hemiptera: Aphididae) with descriptions of a new species from Iran. Insects 16: 68. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/insect....
38.
Karl E., Zamfirov T., Kacharmazov V. 1978. Beobachtungen zum Auftreten der Erdbeerknotenhaarlaus (Pentatrichopus fragaefolii (Cock.)) in verschiedenen Bezirken der DDR. Archiv Phytopathologie Pflanzenschutz 14(5): 333–335.
39.
Kaszyca-Taszakowska N., Depa Ł. 2019. Macrosiphoniella pulvera (Walker, 1848) an aphid species (Hemiptera: Aphididae) new to the Polish fauna. Annals of the Upper Silesian Museum Entomology 28: 1–3. DOI: http://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.....
40.
Kim S., Jung J.K., Park I., Lee B.W., Kim Y.H. 2024. Integrated identification and genetic diversity of potentially invasive clearwing moths (Lepidoptera: Cossoidea: Sesiidae) in Korea. Insects 15: 79. DOI: http://doi.org/10.3390/insects....
41.
Krczal H. 1979. Transmission of the Strawberry Mild Yellow Edge and Strawberry Crinkle Virus by the Strawberry Aphid Chaetosiphon fragaefolli. Acta Horticulturae 95: 23–30.
42.
Krczal H. 1982. Investigations on the biology of the strawberry aphid (Chaetosiphon fragaefolii), the most important vector of strawberry viruses in West Germany. Acta Horticulturae 129: 63–68.
43.
Lee W., Kim H., Lim J., Choi H.-R., Kim Y., Kim Y.-S., Ji J.-Y., Foottit R.G., Lee S. 2011. Barcoding aphids (Hemiptera: Aphididae) of the Korean Peninsula: updating the global data set. Molecular Ecology Resources 11(1): 32–37.
44.
Lee M., Kanturski M., Santammavong C., Lee S. 2024. The First Report of the Aphid Genus Macromyzus (Hemiptera: Aphididae) from Laos, with a Description of a New Species and Its Taxonomic Position. Insects 15: 1015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/insect....
45.
Krokene P., Bente Brurberg M., Flø D., Hatteland B.A., Magnusson C. et al. 2021. Pest risk categorization – New plant health regulations for Norway. Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Plant Health. VKM Report 2021:09, ISBN: 978-82-8259-363-2, ISSN: 2535–4019. Norwegian Scientific Committee for Food and Environment (VKM), Oslo, Norway.
46.
Kumar S., Stecher G., Tamura K. 2016. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Molecular Biology and Evolution 33: 1870–1874.
47.
Lavandero B., Rojas P., Ramirez C.C., Salazar M., Caligari P.D. 2012. Genetic structure of the aphid, Chaetosiphon fragaefolii, and its role as a vector of the Strawberry yellow edge virus to a native strawberry, Fragaria chiloensis in Chile. Journal of Insect Science (Madison) 12: 110.
48.
Milenković S. 1993. Jagodina lisna vaš Chaetosiphon fragaefolii Cockerell u zasadima u Srbiji. Zaštita Bilja 44 (4): 319–323.
49.
Miyazaki M. 1971. A Revision of the tribe Macrosiphini of Japan (Homoptera : Aphididae, Aphidinae). Insecta Matsumurana 34 (1): 1–247.
50.
Muirhead J.R., Gray D.K., Kelly D.W., Ellis S.M., Heath D.D., MacIsaac H.J. 2008. Identifying the source of species invasions: sampling intensity vs. genetic diversity. Molecular Ecology 17 (4): 1020–1035. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365....
51.
Nault L.R. 1997. Arthropod transmission of plant viruses–a new synthesis. Annals of the Entomological Society of America 90: 521–541.
52.
Ng J.C.K., Perry K.L. 2004. Transmission of plant viruses by aphid vectors. Molecular Plant Pathology 5: 505–511. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1364....
53.
Nieto Nafría J.M. 1976. The aphids (Hom: Aphidinea) of cultivated plants in Spain, I: roses, strawberries, raspberries. Boletin del Servicio de Defensa contra Plagas e Inspeccion Fitopatologica 2 (1): 97–112.
54.
Nieto Nafría, J.M., Díaz Gonzáles T.E., Mier Durante M.P. 1984. Catalogue of the aphids (Homoptera Aphidoidea) of Spain and of their food-plants. In: Catálogo de los pulgones (Homoptera, Aphidoidea) de España y de sus plantas hospedadoras. León,Spain, Universidad de León, 174 pp.
55.
Osiadacz B., Wieczorek K. 2006. Myzocallis (Lineomyzocallis) walshii Monell, 1879 (Hemiptera, Aphidoidea), an aphid species new to Poland. Polish Journal of Entomology 75: 233–238.
56.
Osiadacz B., Wojciechowski W. 2008. Aphids (Hemiptera: Aphidinea) of the Ojców National Park: structure and origin of fauna: the monograph. Annals of the Upper Silesian Museum in Bytom Natural History, no. 18. ISSN 0068-466X, 172 pp.
57.
Panzavolta T., Bracalini M., Benigno A., Moricca S. 2021. Alien Invasive Pathogens and Pests Harming Trees, Forests, and Plantations: Pathways, Global Consequences and Management. Forests 12 (10): 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12101....
58.
Remaudière G., Remaudière M. 1997. Catalogue des Aphididae du monde Homoptera Aphidoidea. Institut national de la Recherche scientifique, Paris, France, 474 pp.
59.
Rondon S.I., Cantliffe D.J. 2004. The strawberry aphid, Chaetosiphon fragaefolli (Homoptera: Aphididae): a new pest for the strawberry crop in Florida. Florida Entomologist 87: 612–615.
60.
Rondon S., Cantliffe D.J., Krey K.L., Renkema J.M. 2022. Biology and Control of the Strawberry Aphid, Chaetosiphon fragaefolli (Cockerell) (Homoptera: Aphididae) in Florida. UF/IFAS Extension Publication, HS1009, reviewed 01.01.2022.
61.
Rozas J., Ferrer-Mata A., Sánchez-DelBarrio J.C., Guirao-Rico S., Librado P., Ramos-Onsins S.E., Sánchez-Gracia A. 2017 DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Molecular Biolology and Evolution 34: 3299–3302.
62.
Simon J-C., Carre S., Boutin M., Prunier-Leterme N., Sabater-Munoz B., Latorre A., Bournoville R. 2002. Host-based divergence in populations of the pea aphid: insights from nuclear markers and the prevalence of facultative symbionts. Proceedings of the Biological Society 270 (1513): 1703–1712. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2....
63.
Starowicz M., Kanturski M., Junkiert Ł., Wieczorek K. 2015. Aphids (Hemiptera: Aphidomorpha) of the Botanic Garden of the Jagiellonian University, Kraków. Polish Journal of Entomology 84: 325–338.
64.
Tashev D.G. 1985. A catalogue of host plants of the Bulgarian aphids. Annals of University of Sofia 7685–124.
66.
Trela J., Herczek A. 2014. The zoocenotic structure of aphids (Hemiptera, Sternorrhyncha, Aphidomorpha) in the selected plant comunnities of the Landscape Park “Cistercian Landscape Compositions of the Great Rudas” - monograph. Zespół Parków Krajobrazowych Województwa Śląskiego w Katowicach z/s w Będzinie, Katowice, 180 pp. (in Polish).
67.
Wieczorek K. 2011. Aphid species alien to Poland. Polish Journal of Entomomoly 80: 203–224. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/v10200....
68.
Wieczorek K., Fulcher T.K., Chłond D. 2019. the composition of the aphid fauna (Insecta, Hemiptera) of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Scientific Reports 9: 10000. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598....
69.
Wieczorek K., Chłond D. 2019. Description of the previously unknown sexual morphs of Eucarazzia elegans from Iran and Pakistan and the northernmost record of viviparous generation from Europe. Bulletin of Insectology 72 (2): 177–186.
70.
Wieczorek K., Ball K., Durak R., Borowiak-Sobkowiak B. 2024. New alien and invasive bamboo aphid species of the genus Takecallis (Hemiptera: Aphididae) recorded in Poland – morphological and molecular identity. Journal of Plant Protection Research 64 (1): 69–76. DOI: https://doi.org/10.24425/jppr.....
71.
Wojciechowski W., Depa Ł., Imiolczyk-Cessak S. 2011. Four aphid species (Hemiptera: Aphididae) new to Poland from the Tatra National Park. Polish Journal of Entomology 10: 185–190.
72.
Wojciechowski W., Depa Ł., Halgoš J., Matečný I., Lukáš J., Kanturski M. 2016. Aphids of Slovakia. Distributional catalogue, checklist, keys and list of host plants. Comenius University in Bratislava, Slovakia, ISBN 978-80-223-4263-6, 346 pp.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.