ORIGINAL ARTICLE
The effect of Hortia oreadica Groppo (Rutaceae) extracts on the growth, feeding and digestive enzymes of Anticarsia gemmatalis Hübner [1818] (Erebidae)
1
Institute of Biological and Health Sciences, Universidade Federal de Viçosa / Campus Rio Paranaíba, MG 230, Km 7, 38810-000, Rio Paranaíba, Brazil
2
Institute of Agricultural Sciences, Universidade Federal de Viçosa / Campus Rio Paranaíba, MG 230, Km 7, 38810000, Rio Paranaíba, Brazil
3
Chemistry Institute, Universidade Federal de Goiás, Avenida Esperança, 74690-900, Goiania, Brazil
4
Institute of Exact and Technological Sciences, Universidade Federal de Viçosa / Campus Rio Paranaíba, MG 230, Km 7, 38810000, Rio Paranaíba, Brazil
A - Research concept and design; B - Collection and/or assembly of data; C - Data analysis and interpretation; D - Writing the article; E - Critical revision of the article; F - Final approval of article
Submission date: 2025-03-20
Acceptance date: 2025-07-11
Online publication date: 2025-07-30
Corresponding author
Liliane Evangelista Visotto
Institute of Biological and Health Sciences, Universidade Federal de Viçosa / Campus Rio Paranaíba, MG 230, Km 7, 38810-000, Rio Paranaíba, Brazil
Institute of Biological and Health Sciences, Universidade Federal de Viçosa / Campus Rio Paranaíba, MG 230, Km 7, 38810-000, Rio Paranaíba, Brazil
HIGHLIGHTS
- H. oreadica extracts showed activity against A. gemmatalis
- HE is the most effective, causing the greatest mortality
- Biological parameters were negatively affected by HE and DEAE extracts
- HE negatively affected the insect's nutritional indices and enzymatic activities
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
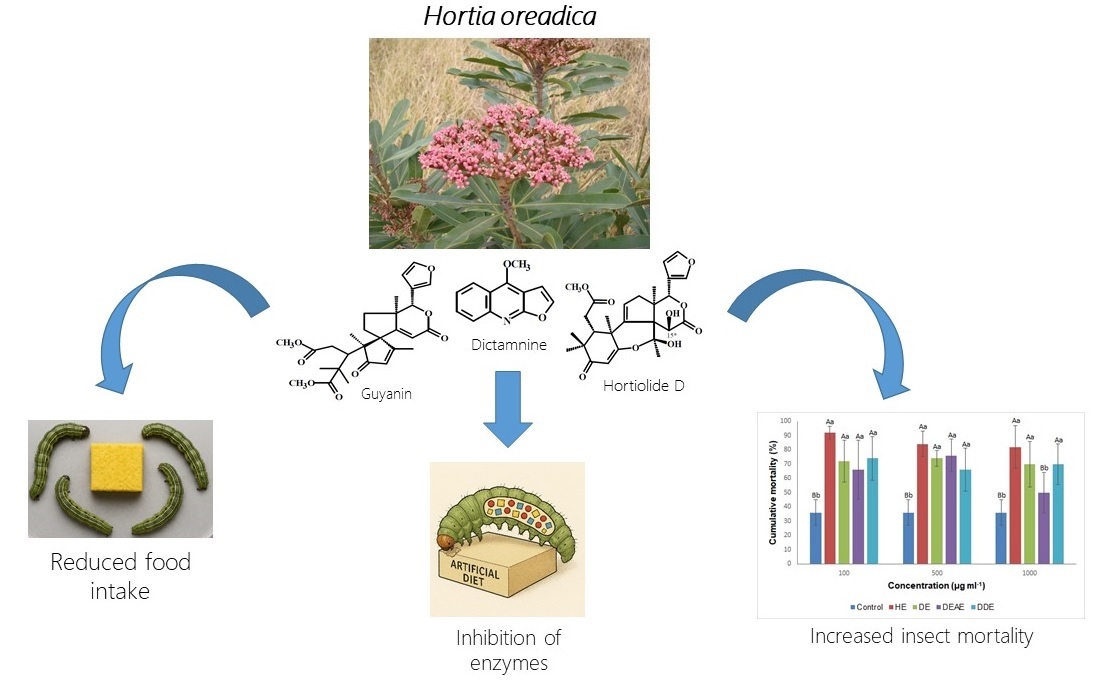
The effects of four extracts of Hortia oreadica Groppo (Rutaceae) on the biological parameters, nutritional indices, and activity of digestive enzymes of Anticarsia gemmatalis Hübner [1818] (Erebidae) were evaluated. Newly hatched caterpillars were subjected to extracts from H. oreadica extracted with hexane (HE), dichloromethane (DE), dichloromethane fractionated with ethyl acetate (DEAE) and dichloromethane fractionated with dichloromethane (DDE) at concentrations 0, 100, 500 and 1000 µg ml-1. The results showed that treatments significantly increased the cumulative mortality rate of A. gemmatalis and that HE 100 µg ml-1 was the most effective, causing 92% of insects’ deaths. The period of larval development was significantly shorter with treatments HE 100 and 500 µg ml-1 and longer with DEAE (all concentrations). The pupal weight was lower in the treatments HE 1000 µg ml-1 and in all doses tested of the DEAE treatment. The morphological integrity of pupae and adults was not affected. The lowest values of relative food consumption rate, relative metabolic rate, and relative growth rate were observed in the HE 100 µg ml-1 treatment. In most treatments, there was a reduction in the activity of total proteases, serine and cysteine proteases, and amylase. The results suggest that the HE extract of H. oreadica is the most efficient in controlling A. gemmatalis, due to the presence of deterrent metabolites that affect the insect's digestion and nutrition and consequently promote adverse effects on its development and mortality.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have declared that no conflict of interests exist.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.